Introductory Overview to Marine Loading Arms
In the dynamic and intricate world of shipping, the efficient and safe transfer of liquids between vessels and shore-based facilities is of paramount importance. To meet the demands of modern shipping and ensure the safety of cargo operations, the maritime industry relies on advanced equipment and technologies. Marine Loading Arms (MLA) have become indispensable tools that expedite the loading and unloading of various fluids, in a wide range of viscosities and temperatures, ranging from crude oil and chemicals to liquefied natural gas ( LNG) and refined petroleum.
Marine loading arms are flexible enough to accommodate any movement of the vessel during loading/unloading. These hydraulically operated marine loading arms are equipped with couplings and emergency release systems and meet the fastest and safest loading/unloading requirements.
By providing a seamless connection between vessels and terminals, MLAs have revolutionized the way liquid cargo is transferred, ensuring a fast, reliable and secure process.
Functionality of marine loading arms
In essence, a marine loading arm is a specialized mechanical system designed to transfer fluids from a storage facility or terminal to a vessel, or vice versa. Unlike traditional methods involving hose lines and gantry cranes, marine loading arms offer a more controlled and safer process. They are designed with multiple degrees of freedom, allowing them to move in various directions, including the vertical, horizontal, and rotation axes. This exceptional mobility gives MLAs the flexibility to adapt to different vessel sizes, tidal variations, and weather conditions, ensuring a consistent and reliable transfer operation.
Features of marine loading arms
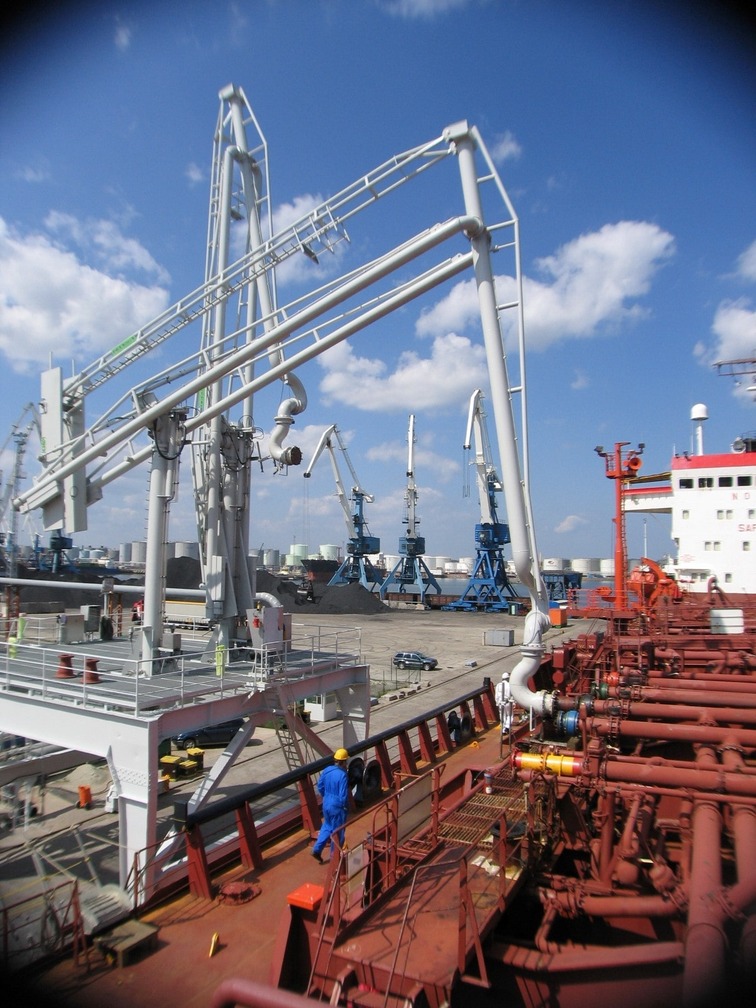

Marine loading arms should be specified/designed to account for movement of the tanker during loading/unloading due to tides/waves/wind and increase/decrease in load. Each loading arm is built with a certain operating envelope in mind. If a connected loading arm is forced out of this envelope, it should be immediately disconnected (manually or automatically on some systems). Key elements influencing the required operating envelope include the DWT of the tanker, tidal range, maximum wave height, dock construction elevation, and the size/number of loading arms on the jetty.
Marine loading arms are often hydraulically powered. A hydraulic system, which often services all of the loading arms on a jetty side, is used to move the arms into position on the ship's deck and to retract the arms after use.
For loading/unloading of small barges, usually only a marine loading arm is used. While for VLCC several are used (up to 4 marine loading arms in parallel).
Marine Loading Arm Components
A typical marine loading arm consists of several essential components, each contributing to its functionality and safety:
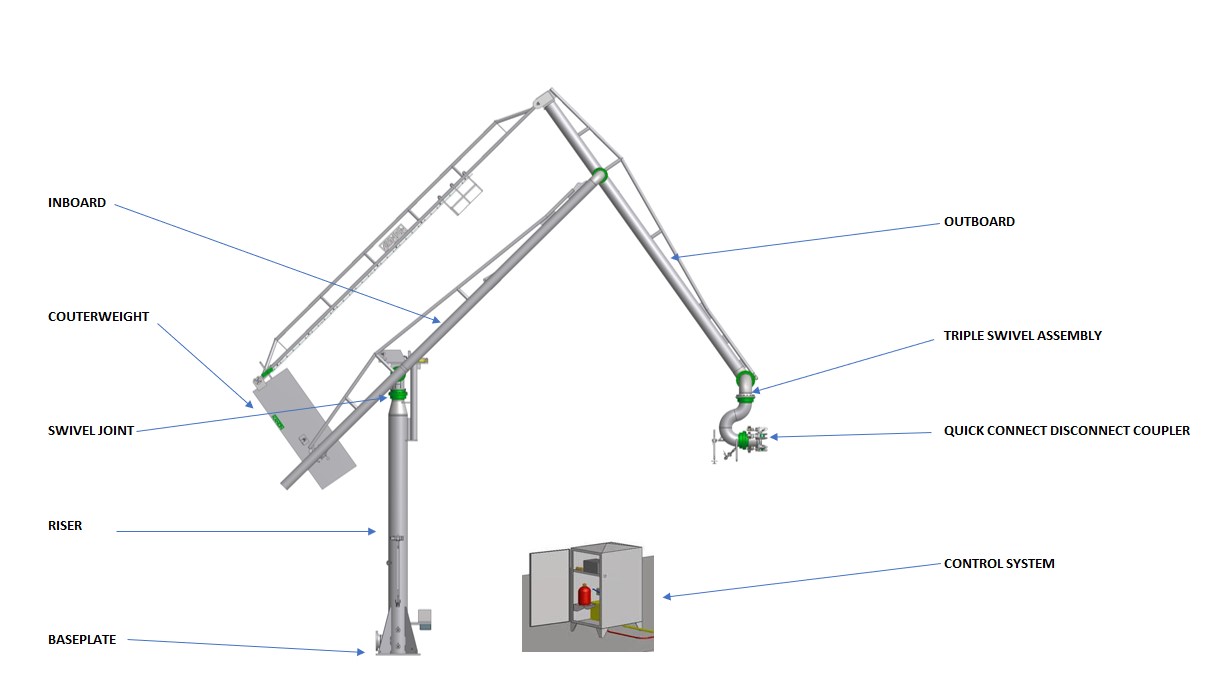
- Swivel Joints : High quality pipes and swivel joints are used to transport the fluid from the shore facility to the vessel or vice versa. Swivel joints allow for rotation, allowing the loading arm, once attached, to follow the movements of the vessel within the work area. Swivel joints must be lubricated for life and the male and female parts must have the same mechanical hardness.
- Counterweight SystemThe counterweight system ensures the MLA remains balanced and stable during operation, improving safety and reducing operator fatigue. Only a single counterweight should be used, as a secondary counterweight could collide with the cabin of a small barge.
- Control System: A sophisticated control system governs the movement and operation of the MLA. This system is often equipped with automation features, which ensures accurate alignment and prevents potential accidents.
- Quick Connect Disconnect Coupler (QCDC): Offers the ability to connect the MLA to the ship's manifold. They exist in a manual version, normally for small MLA diameters, and in a hydraulic version. A multisize QCDC can be proposed, as sometimes the dock receives a ship with smaller manifold diameters than usual.
- Emergency Release System (ERC) : To mitigate risks in case of unforeseen events, MLAs are equipped with emergency release systems that allow for a quick emergency disconnect between the ship and the MLA. For safety reasons, ball valves are used. Butterfly valves and disc valves are not HAZOP safe.
Optional Equipment : Marine loading arms are often accompanied by an gangway access system, which provides safe passage for personnel between the ship and the terminal, and by quick release mooring hooks.
Design codes for marine loading arms
Advantages of marine loading arms
Marine loading arms offer a plethora of advantages that have contributed to their widespread adoption:
- Efficiency: MLAs allow for fast loading and unloading operations, reducing vessel downtime and increasing overall operational efficiency.
- Safety: Precise control and automation of marine loading arms minimize human error and ensure a safe working environment for operators. Emergency release systems further enhance security measures.
- Flexibility: Marine loading arms can accommodate various sizes and types of vessels, making them adaptable to different liquid cargo transfer requirements.
- Maintenance: High-quality marine loading arms are built to last and require minimal maintenance, reducing operating costs in the long run.
- Environmental Protection : The process of sealed and controlled transfer of marine loading arms reduces the risk of spills and leaks, contributing to the conservation of the environment.
Conclusion
If you have any questions, please contact us via Whatsapp, our contact form, or our datasheet. We will be glad to help you.
